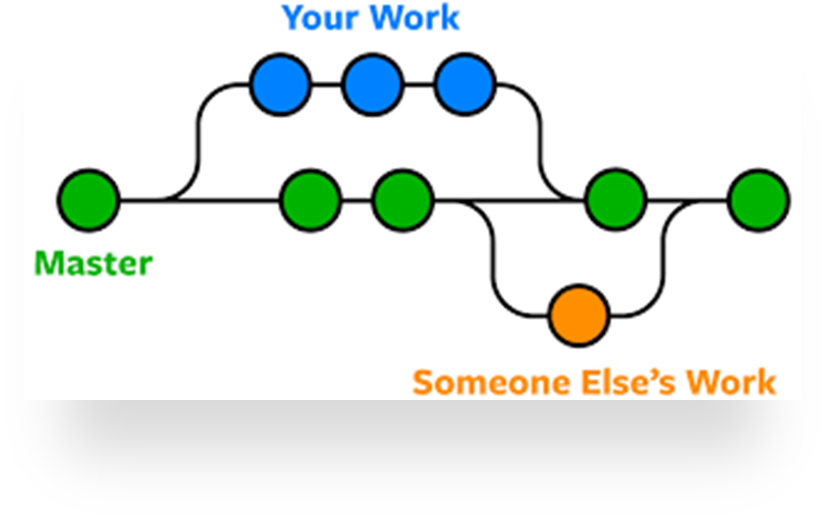
What is Git Branch?
- A branch in Git is simply a lightweight movable pointer to one of the commits.
- Master branch always points to the last commit you made on.
Git Commands | Description |
Git branch -a | – List all of your branches. |
Git branch [name] | – Creating a new branch at the current commit. |
Git checkout [branch-name] | – Switch to another branch. |
Git checkout -b [name] | – Create a new branch and switch to it at the moment. |
Git merge [branch] | – Unstage a file while retaining the changes in working directory. |
Git merge [branch] –no-ff | – Create a merge commit in all cases. No fast-forward. |
Git log | – Show all commits in the current branch’s history. |
Creating & Switching to a New Branch
- Here is an example of creating a new branch called “Development”:
# git branch -a
# git checkout -b development
(Creating New Branch) --> # git branch development
(Switching to New Branch) --> # git checkout development
# vi development.txt : “test of development branch”
# git add development.txt
# git commit -m “development test commit”
# git status
On branch development
nothing to commit, working tree clean
# git checkout master
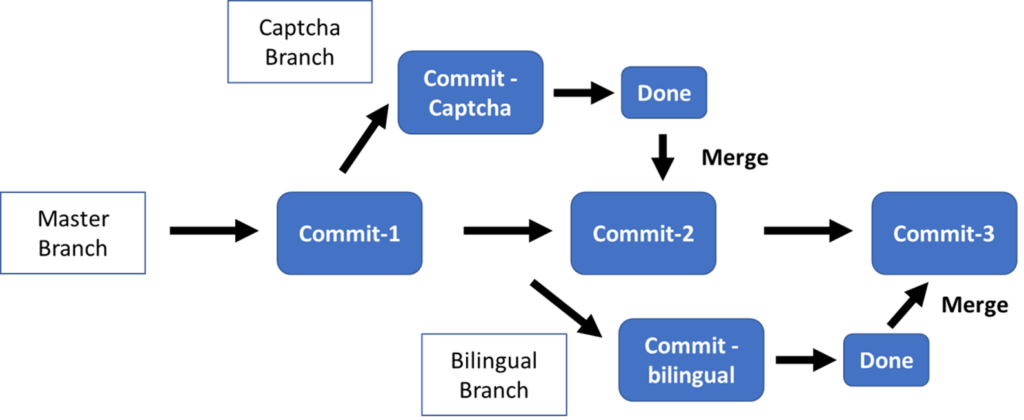
Merging Two Branches Together
- How to merge Development branch with Master branch:
i.First, switch to Master Branch:
# git checkout master
Switched to branch 'master'
i.Then, merge Development branch in Master branch:
# git merge development --no-ff
Updating 3c1599c..5292e50
Fast-forward
development.txt | 1 +
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 development.txt
